
Azilsartan Suppressed LPS-Induced Inflammation in U937 Macrophages through Suppressing Oxidative Stress and Inhibiting the TLR2/MyD88 Signal Pathway | ACS Omega
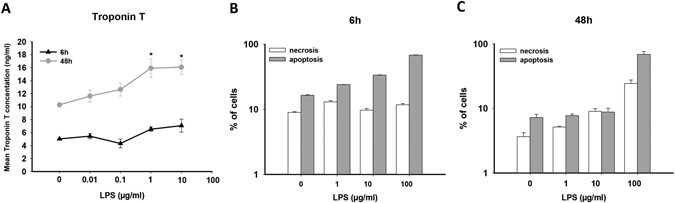
Lipopolysaccharides induced inflammatory responses and electrophysiological dysfunctions in human-induced pluripotent stem cell derived cardiomyocytes | Scientific Reports
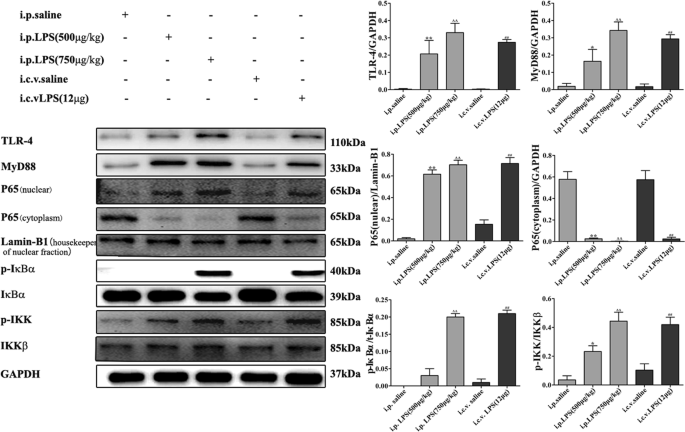
Neuroinflammation induced by lipopolysaccharide causes cognitive impairment in mice | Scientific Reports
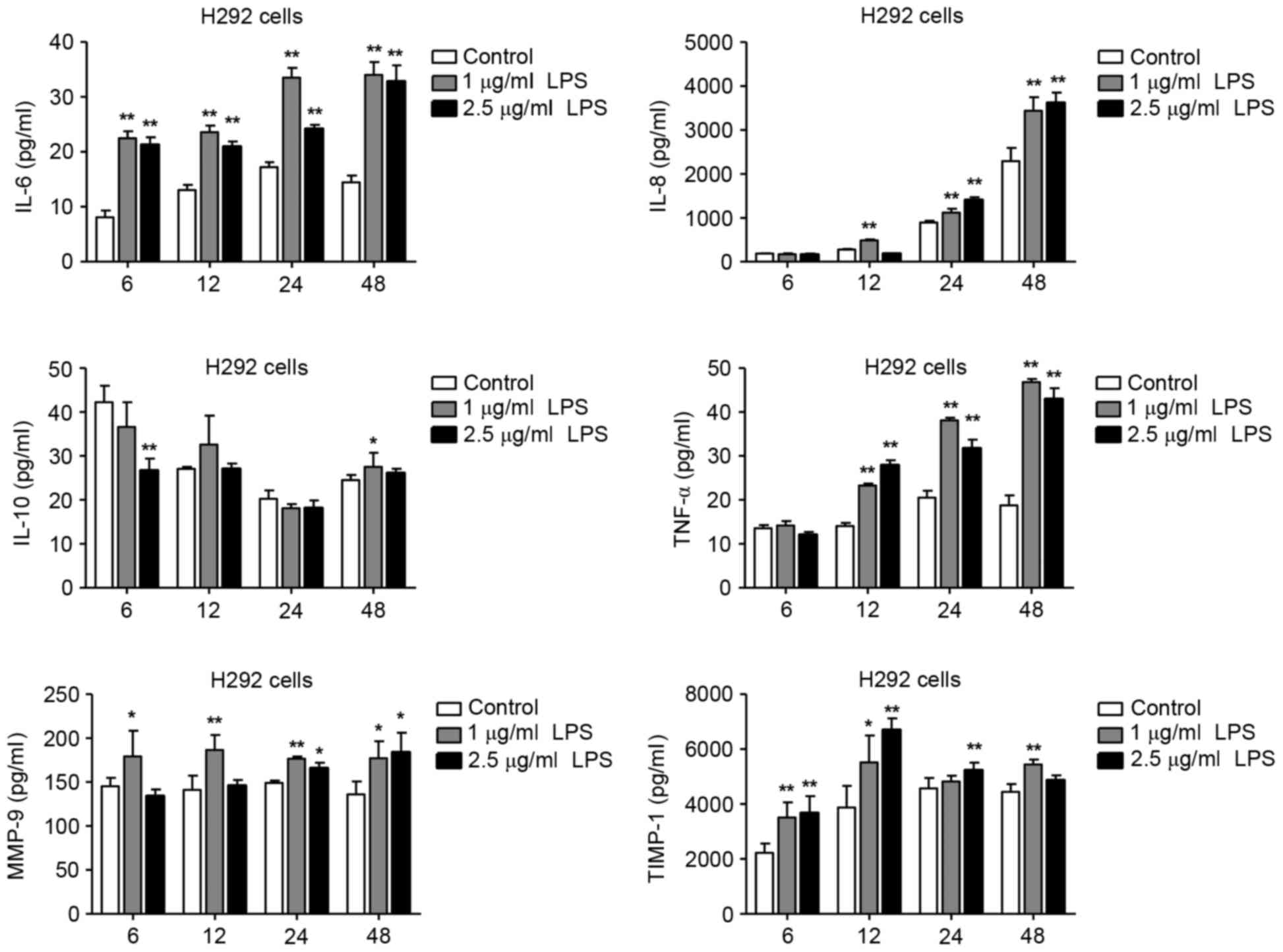
LPS‑induced proinflammatory cytokine expression in human airway epithelial cells and macrophages via NF‑κB, STAT3 or AP‑1 activation

Surfactant Protein A Enhances the Degradation of LPS-Induced TLR4 in Primary Alveolar Macrophages Involving Rab7, β-arrestin2, and mTORC1 | Infection and Immunity

Surfactant Protein A Enhances the Degradation of LPS-Induced TLR4 in Primary Alveolar Macrophages Involving Rab7, β-arrestin2, and mTORC1 | Infection and Immunity

Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Microglial Activation and Neuroprotection against Experimental Brain Injury Is Independent of Hematogenous TLR4 | Journal of Neuroscience
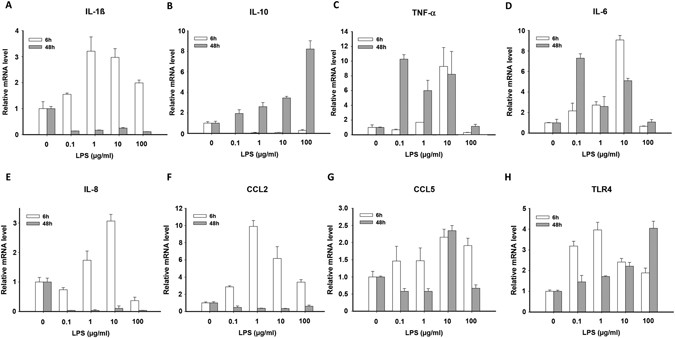
Effect of LPS-treatment on pro-inflammatory cytokine/chemokine levels.... | Download Scientific Diagram

A Novel Anti-inflammatory Phenotype Transformed by Repetitive Low-dose Lipopolysaccharide in Primary Peritoneal Tissue-resident Macrophages | Anticancer Research
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced Biliary Epithelial Cell NRas Activation Requires Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) | PLOS ONE
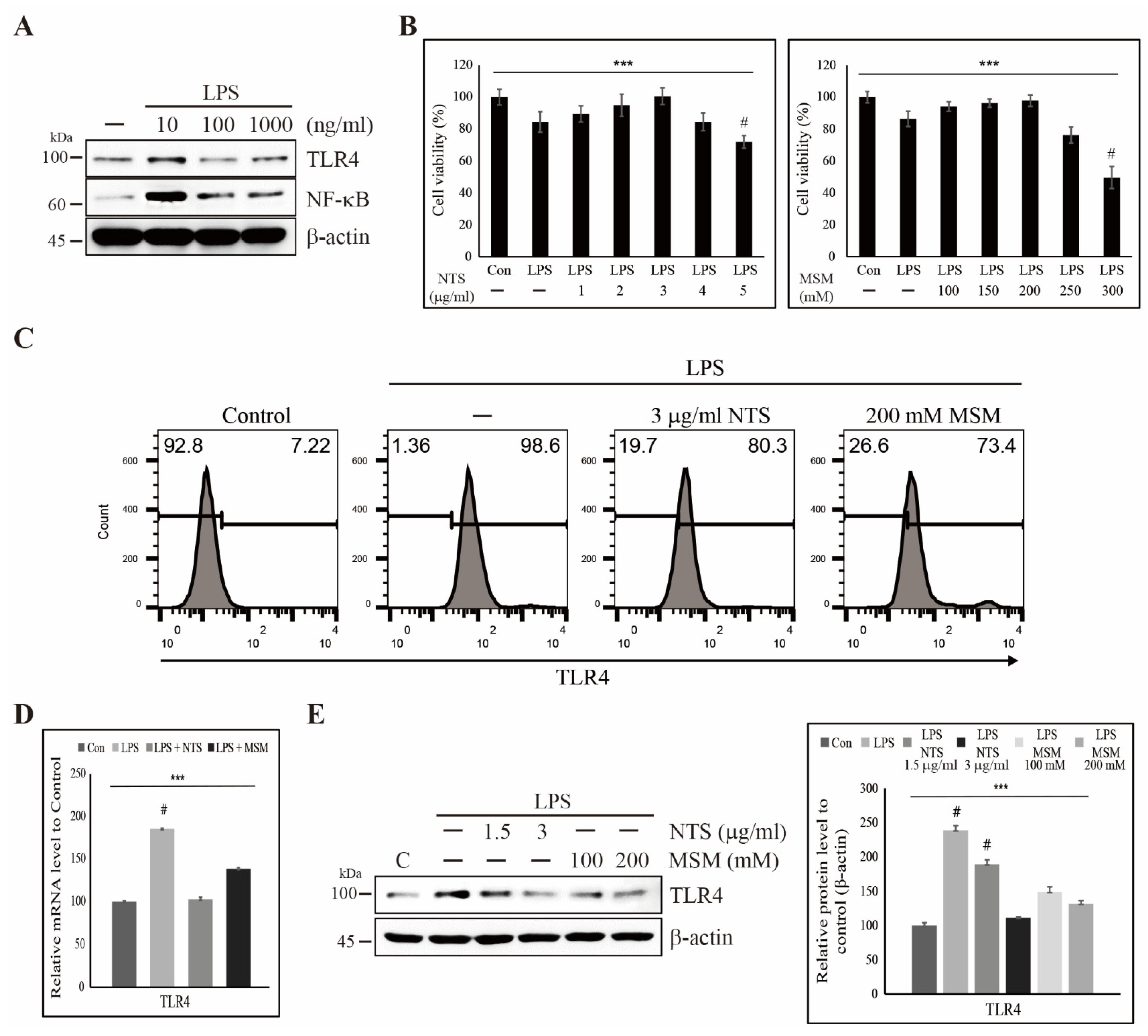
Life | Free Full-Text | Natural Sulfurs Inhibit LPS-Induced Inflammatory Responses through NF-κB Signaling in CCD-986Sk Skin Fibroblasts
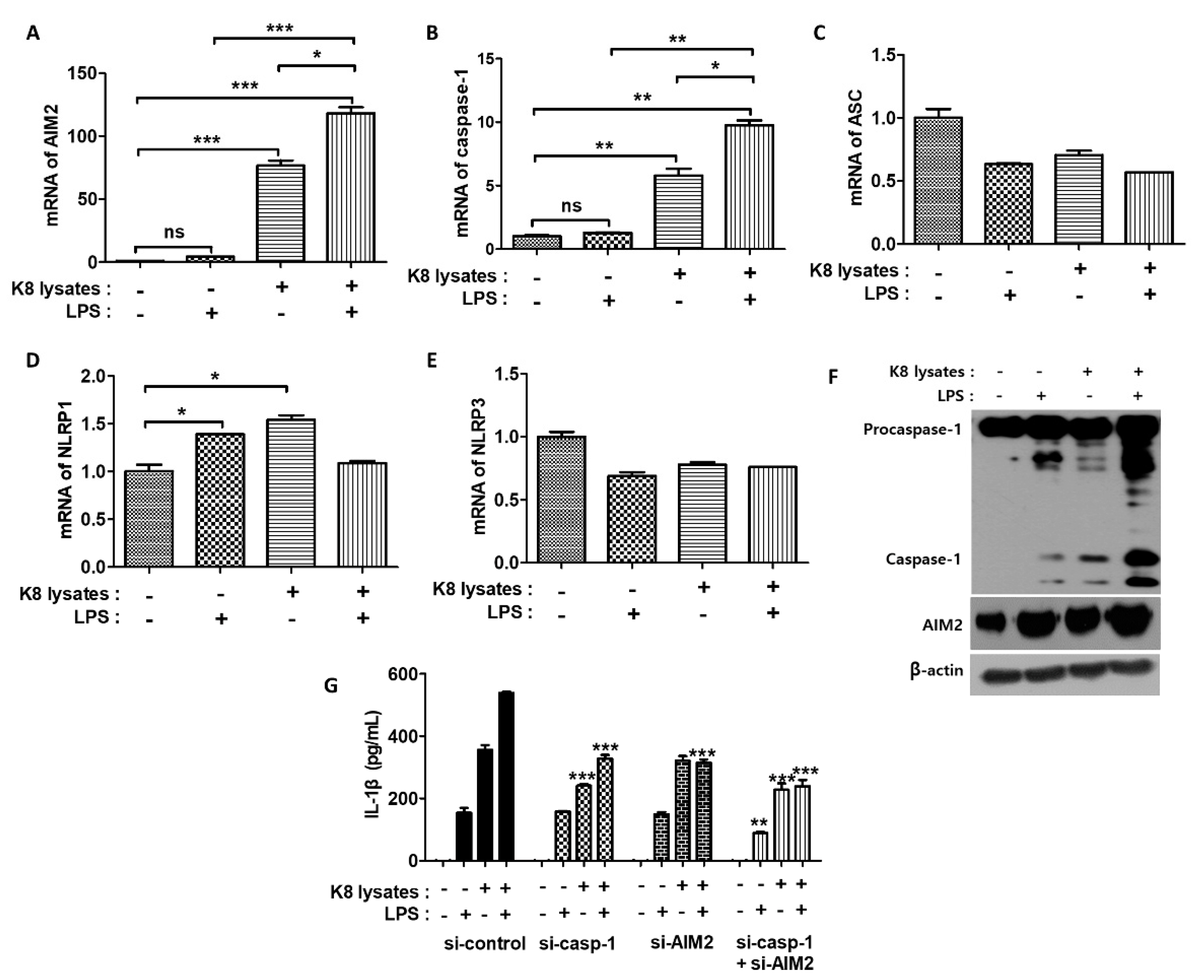
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Alleviation of LPS-Induced Inflammation and Septic Shock by Lactiplantibacillus plantarum K8 Lysates

Ginsenoside Rg1 attenuates LPS-induced cognitive impairments and neuroinflammation by inhibiting NOX2 and Ca2+–CN–NFAT1 signaling in mice - ScienceDirect

A unique hybrid characteristic having both pro- and anti-inflammatory phenotype transformed by repetitive low-dose lipopolysaccharide in C8-B4 microglia | Scientific Reports
Lipopolysaccharides induced inflammatory responses and electrophysiological dysfunctions in human-induced pluripotent stem cell derived cardiomyocytes | Scientific Reports

The LPS-Induced Transcriptional Upregulation of the Chicken Lysozyme Locus Involves CTCF Eviction and Noncoding RNA Transcription: Molecular Cell

Lipopolysaccharides induced inflammatory responses and electrophysiological dysfunctions in human-induced pluripotent stem cell derived cardiomyocytes | Scientific Reports
SRV2 promotes mitochondrial fission and Mst1-Drp1 signaling in LPS-induced septic cardiomyopathy | Aging
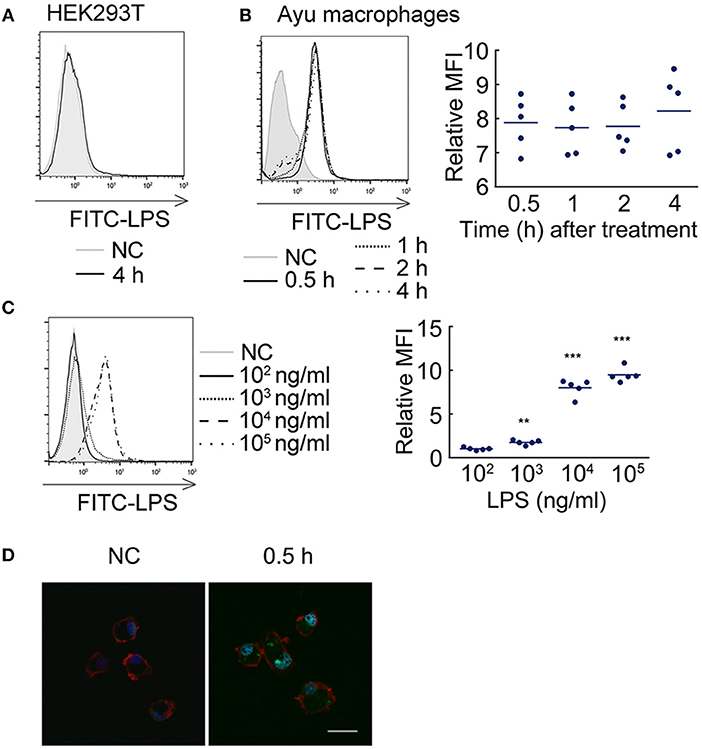
Frontiers | A Novel Lipopolysaccharide Recognition Mechanism Mediated by Internalization in Teleost Macrophages
Dexmedetomidine inhibits LPS-induced proinflammatory responses via suppressing HIF1α-dependent glycolysis in macrophages | Aging
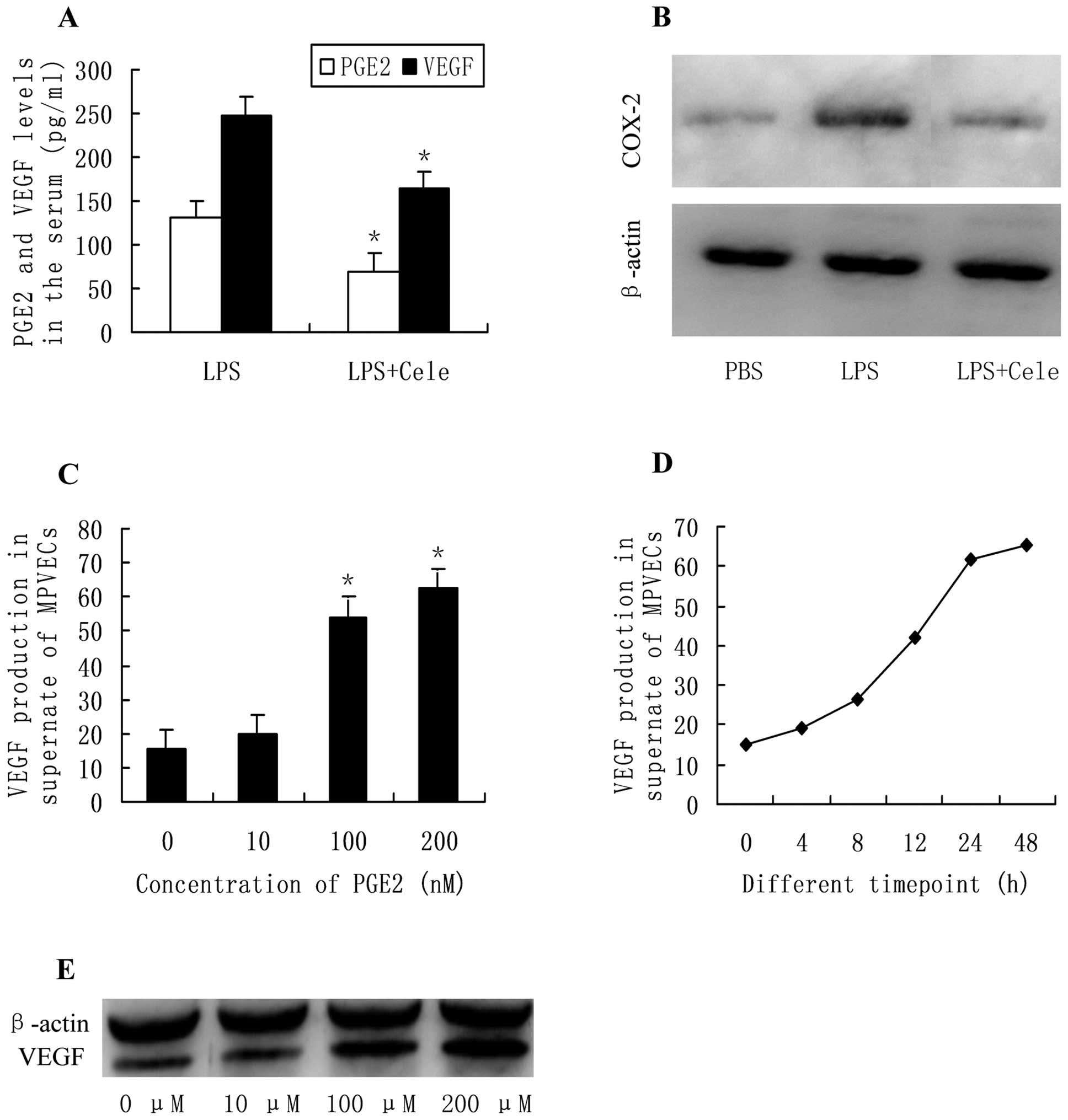
Lipopolysaccharide induces inflammation and facilitates lung metastasis in a breast cancer model via the prostaglandin E2-EP2 pathway

